INDEX
Exp. No.
|
Experiment Name
|
01
|
Configuring Basic
Router Settings With IOS CLI.
|
02
|
Observing Static Routing With Three Routers
with CLI.
|
03
|
Configuring
RIP Version-1 with CLI using Three Routers Connected in Delta Connection.
|
04
|
Configuring RIP
Version-2 with CLI.
|
05
|
Configuring VLAN with
CLI.
|
EXPERIMENT
NO: 01
EXPERIMENT NAME: Configuring Basic Router
Settings with IOS CLI.
OBJECTIVE: The objective of
the lab is to configure a simple network to allow two PC to send & receive
packets among each other.
THEORY: Router
is the backbone of a network. Properly configuring the router will protect
one’s information from prying eyes, securely connect all of the devices to the
internet.
CONNECTION:
CLI COMMAND:
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog?
[yes/no]: no
Press RETURN to get started!
Router>enable
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#hostname Router0
Router0(config)#enable secret class
Router0(config)#line con 0
Router0(config-line)#password cisco
Router0(config-line)#login
Router0(config-line)#exit
Router0(config)#line vty 0 4
Router0(config-line)#password cisco
Router0(config-line)#login
Router0(config-line)#exit
Router0(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
Router0(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router0(config-if)#description Router0 FastEthernet0/0
Router0(config-if)#no shutdown
Router0(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0,
changed state to up
Router0(config-if)#exit
Router0(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1
Router0(config-if)#ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router0(config-if)#description Router0 FastEthernet0/1
Router0(config-if)#no shutdown
Router0(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/1, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/1,
changed state to up
Router0(config-if)#exit
Router0(config)#exit
Router0#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router0#
OUTPUT:
CONCLUSION:
The router was configured successfully. When PC1 was
pinged from PC0 it responded back after some time. It was also tested by
sending a message. The message was received and an acknowledgment was sent back
to the sender.
EXPERIMENT NO: 02
EXPERIMENT
NAME: Observing Static
Routing With Three Routers with CLI.
OBJECTIVE:
The objective of the lab is to
configure 4 routers to observe static routing among 4 different networks.
THEORY:
Static
routing is a form of routing that occurs when a router uses a manually-configured
routing entry, rather than information from dynamic routing traffic. It’s
easy to implement in a small network, suitable for simple topologies or for
special purposes such as a default static route.
CONNECTION:
OUTPUT:
CLI COMMAND:
-----------------------------------------------------Router0-----------------------------------------
Router>enable
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add
192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 10.0.0.2
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/0, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.11.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.3
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.12.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.3
Router(config)#ip route 11.0.0.0
255.0.0.0 10.0.0.3
Router(config)#ex
Router#
-----------------------------------------------------Router1----------------------------------------------
Router>enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add
192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 10.0.0.3
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.0.0.2
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/1, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.10.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.0.2
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.12.0
255.255.255.0 11.0.0.3
Router(config)#ex
Router#
-----------------------------------------------------Router2----------------------------------------------
Router>enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add
192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.0.0.3
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.11.0
255.255.255.0 11.0.0.2
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.10.0
255.255.255.0 11.0.0.2
Router(config)#10.0.0.0
255.255.255.0 11.0.0.2
Router(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0
255.0.0.0 11.0.0.2
Router(config)#ex
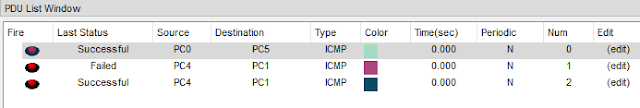
CONCLUSION:
The routers were configured successfully. It was tested
by sending messages several times. The message was received and an acknowledgment
was sent back to the sender. The system was built using static routing where I
configured the router with CLI. The IP route was set by giving destination
network, subnet mask, and next hop.
EXPERIMENT NO: 03
EXPERIMENT
NAME: Configuring RIP Version-1 with Three Routers Connected
in Delta Connection.
OBJECTIVE: The
objective of the lab is to configure 3 routers to observe RIPv1 and observe the output. Also, compare with static routing.
THEORY: RIPv1 uses local broadcasts to share routing
information. These updates are periodic in nature, occurring, by default, every
30 seconds. To prevent packets from circling around a loop forever, both
versions of RIP solve counting to infinity by placing a hop count limit of 15
hops on packets. Any packet that reaches the sixteenth hop will be dropped. RIP
supports up to six equal-cost paths to a single destination. Equal-cost path
is the paths where the metric is the same (Hop count).
CONNECTION:
CLI COMMAND:
------------Router 0-----------
Router>enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int serial 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 10.0.0.1
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/0, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.1
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/1, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#no a
Router(config-router)#no
auto-summary
Router(config-router)#network
10.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network
192.168.1.0
Router(config-router)#network
12.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router#
----------Router 1----------
----------Router 1----------
Router>enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int s 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 10.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router#
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#no auto-summary
Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.2.0
Router(config-router)#network 11.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router#
-----------Router 2------------
Router>enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int fa 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 192.168.3.1
255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutd
Router(config-if)#
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add 11.0.0.2
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#int s 0/0/1
Router(config-if)#ip add 12.0.0.2
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shut
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0/1,
changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ex
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#no a
Router(config-router)#network
11.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network
12.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network
192.168.3.0
Router(config-router)#ex
Router(config)#ex
OUTPUT:
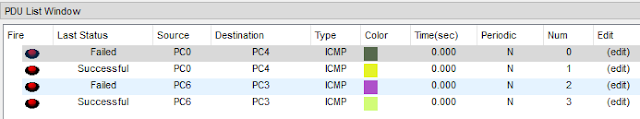
CONCLUSION:
Both
static routing and RIPv1 was configured using a delta connection. In rip, the
shortest route was selected automatically. But in the static connection, we need to
specify all the networks with the next hop. Also in rip if one path was
destroyed it searched for an available route to the destination and sent the data,
which wasn’t the case with static routing.
EXPERIMENT NO.: 04
EXPERIMENT NAME: Configuring RIP Version-2 using CLI.
OBJECTIVE:
The objective of the lab is to configure routers using CLI
to observe RIPv2.
THEORY:
RIPv2
is a distance
vector routing protocol with routing enhancements built into it, and it
is based on RIPV1. Therefore, it is commonly called as hybrid
routing protocol.
RIPv2
uses multicasts instead
of broadcasts. RIPv2 supports
triggered updates. When a change occurs, a RIPv2 router will immediately
propagate its routing information to its connected neighbors. RIPv2 is a
classless protocol and it supports variable-length
subnet masking (VLSM).
Both RIPv1 and RIPv2 uses hop count as the metric.
CONNECTION:
CLI COMMAND:
Router>enable
Router#configure
t
Enter
configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface
serial 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip
ad 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no
shutdown
%LINK-5-CHANGED:
Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#interface
fastEthernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip
address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.192
Router(config-if)#no
shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED:
Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN:
Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router#
Router#conf
t
Enter
configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router
rip
Router(config-router)#version
2
Router(config-router)#no
auto-summary
Router(config-router)#network
10.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network
192.168.10.0
Router(config-router)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router>enable
Router#configure t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface serial
0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip ad 10.0.0.2
255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
Serial0/0/0, changed state to down
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#interface
fastEthernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address
172.50.1.1 255.255.240.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#ex
Router(config)#ex
Router#
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from
console by console
Router#copy running-config startup-c
Router#copy running-config
startup-config
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#version 2
Router(config-router)#no
auto-summary
Router(config-router)#network
10.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#network
172.50.1.0
Router(config-router)#ex
Router(config)#ex
OUTPUT:
CONCLUSION:
The
message was sent successfully. RIPv2 is classless routing. It supports VLSM, unlike RIPv1. RIPv2 updates carry the next-hop IP address in each route entry.
EXPERIMENT NO: 05
EXPERIMENT NAME: Configuring VLAN with CLI.
OBJECTIVE: The the objective of this experiment is to configure VLAN using CLI and observe the
output.
THEORY: VLAN (Virtual Local Network) is a
logically separate IP sub-network which allows multiple IP networks and subnets
to exist on the same-switched network. A VLAN allows a network of computers and
users to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single
LAN and are sharing a single broadcast and multicast domain. The purpose of
implementing a VLAN is to improve the performance of a network or apply
appropriate security features.
CONNECTION:
CLI COMMAND (FOR 1 ROUTER):
Switch>enable
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one
per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#vlan 10
Switch(config-vlan)#name V10
Switch(config-vlan)#exit
Switch(config)#vlan 11
Switch(config-vlan)#name V11
Switch(config-vlan)#exit
Switch(config)#vlan 12
Switch(config-vlan)#name V12
Switch(config-vlan)#exit
Switch(config)#
Switch(config)#int fa 0/1
Switch(config-if)#sw m a
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 10
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/6
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 10
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/2
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 11
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/5
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 11
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/3
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 12
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/4
Switch(config-if)#sw a vlan 12
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/7
Switch(config-if)#sw m t
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/7, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/7, changed state to up
Switch(config-if)#sw nonegotiate
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#int fa 0/8
Switch(config-if)#sw m t
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/8, changed state to down
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol
on Interface FastEthernet0/8, changed state to up
Switch(config-if)#sw nonegotiate
Switch(config-if)#ex
Switch(config)#ex
Switch#
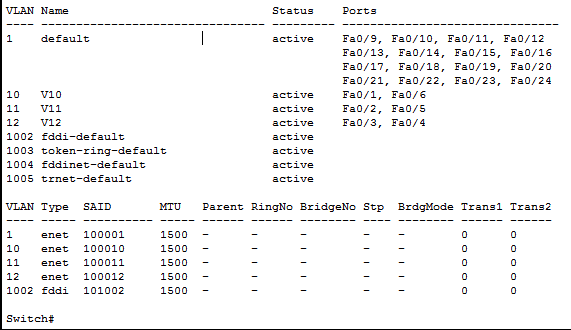
OUTPUT:
CONCLUSION:
VLAN is a subcategory of
VPN and VPN is a means of creating a secured network for safe data
transmission. A VLAN is basically a means to logically segregate networks
without physically segregating them with various switches. Here we connected 3
switches and divided pcs under each switch in 3 network. Then pc connected to
the same switches which are in different VLAN can’t send data among each other.
But pc of the different switch can communicate as long as they’re under the same
VLAN.















No comments:
Post a Comment